Turning on the awslogs log driver for your containers
If you are using the Fargate launch type for your tasks, all you need to do to turn on the awslogs log driver is add the required logConfiguration parameters to your task definition. For more information, see Specifying a log configuration in your task definition.
If you are using the EC2 launch type for your tasks and want to turn on the awslogs log driver, your Amazon ECS container instances require at least version 1.9.0 of the container agent. For information about checking your agent version and updating to the latest version, see Updating the Amazon ECS container agent.
If you are not using the Amazon ECS-optimized AMI (with at least version 1.9.0-1 of the ecs-init package) for your container instances, you also need to specify that the awslogs logging driver is available on the container instance when you start the agent by using the following environment variable in your docker run statement or environment variable file. For more information, see Installing the Amazon ECS container agent.
ECS_AVAILABLE_LOGGING_DRIVERS='["json-file","awslogs"]'Your Amazon ECS container instances also require logs:CreateLogStream and logs:PutLogEvents permission on the IAM role with which you launch your container instances. If you created your Amazon ECS container instance role before awslogs log driver support was enabled in Amazon ECS, then you might need to add this permission. The ecsTaskExecutionRole is used when it is assigned to the task and should contain the correct permissions. For information about checking your task execution role, see To check for the ecsTaskExecutionRole in the IAM console. If your container instances use the managed IAM policy for container instances, then your container instances should have the correct permissions. For information about checking your Amazon ECS container instance role and attaching the managed IAM policy for container instances, see To check for the ecsInstanceRole in the IAM console.
Creating a log group
The awslogs log driver can send log streams to an existing log group in CloudWatch Logs or it can create a new log group on your behalf. The AWS Management Console provides an auto-configure option which creates a log group on your behalf using the task definition family name with ecs as the prefix. Alternatively, you can manually specify your log configuration options and specify the awslogs-create-group option with a value of true which will create the log groups on your behalf.
To use the awslogs-create-group option to have your log group created, your IAM policy must include the logs:CreateLogGroup permission.
The following code shows how to set the awslogs-create-group option.
{
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "firelens-container",
"awslogs-region": "us-west-2",
"awslogs-create-group": "true",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "firelens"
}
}
}Using the auto-configuration feature to create a log group
When registering a task definition in the Amazon ECS console, you have the option to allow Amazon ECS to auto-configure your CloudWatch logs. This option creates a log group on your behalf using the task definition family name with ecs as the prefix.
To use log group auto-configuration option in the Amazon ECS console
- Open the Amazon ECS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ecs/.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Task Definitions, Create new Task Definition.
- Select your compatibility option and choose Next Step.
- Choose Add container.
- In the Storage and Logging section, for Log configuration, choose Auto-configure CloudWatch Logs.
- Enter your awslogs log driver options. For more information, see Specifying a log configuration in your task definition.
- Complete the rest of the task definition wizard.
Available awslogs log driver options
The awslogs log driver supports the following options in Amazon ECS task definitions. For more information, see CloudWatch Logs logging driver.
Required: No
Specify whether you want the log group automatically created. If this option is not specified, it defaults to false.
Required: Yes
Specify the region to which the awslogs log driver should send your Docker logs. You can choose to send all of your logs from clusters in different regions to a single region in CloudWatch Logs so that they are all visible in one location, or you can separate them by region for more granularity. Be sure that the specified log group exists in the region that you specify with this option.
awslogs-group
Required: Yes
You must specify a log group to which the awslogs log driver sends its log streams. For more information, see Creating a log group.
awslogs-stream-prefix
Required: Optional for the EC2 launch type, required for the Fargate launch type.
The awslogs-stream-prefix option allows you to associate a log stream with the specified prefix, the container name, and the ID of the Amazon ECS task to which the container belongs. If you specify a prefix with this option, then the log stream takes the following format:
prefix-name/container-name/ecs-task-idIf you don't specify a prefix with this option, then the log stream is named after the container ID that is assigned by the Docker daemon on the container instance. Because it is difficult to trace logs back to the container that sent them with just the Docker container ID (which is only available on the container instance), we recommend that you specify a prefix with this option.
For Amazon ECS services, you could use the service name as the prefix, which would allow you to trace log streams to the service that the container belongs to, the name of the container that sent them, and the ID of the task to which the container belongs.
You must specify a stream-prefix for your logs in order to have your logs appear in the Log pane when using the Amazon ECS console.
awslogs-datetime-format
Required: No
This option defines a multiline start pattern in Python strftime format. A log message consists of a line that matches the pattern and any following lines that don’t match the pattern. Thus the matched line is the delimiter between log messages.
One example of a use case for using this format is for parsing output such as a stack dump, which might otherwise be logged in multiple entries. The correct pattern allows it to be captured in a single entry.
For more information, see awslogs-datetime-format.
This option always takes precedence if both awslogs-datetime-format and awslogs-multiline-pattern are configured.
Required: No
This option defines a multiline start pattern using a regular expression. A log message consists of a line that matches the pattern and any following lines that don’t match the pattern. Thus the matched line is the delimiter between log messages.
For more information, see awslogs-multiline-pattern.
This option is ignored if awslogs-datetime-format is also configured.
Required: No
Valid values: non-blocking | blocking
Default value: blocking
The delivery mode of log messages from the container to awslogs. For more information, see Configure logging drivers.
max-buffer-size
Required: No
Default value: 1m
When non-blocking mode is used, the max-buffer-size log option controls the size of the ring buffer used for intermediate message storage.
Specifying a log configuration in your task definition
Before your containers can send logs to CloudWatch, you must specify the awslogs log driver for containers in your task definition. This section describes the log configuration for a container to use the awslogs log driver. For more information, see Creating a task definition using the new console.
The task definition JSON shown below has a logConfiguration object specified for each container; one for the WordPress container that sends logs to a log group called awslogs-wordpress, and one for a MySQL container that sends logs to a log group called awslogs-mysql. Both containers use the awslogs-example log stream prefix.
{
"containerDefinitions": [
{
"name": "wordpress",
"links": [
"mysql"
],
"image": "wordpress",
"essential": true,
"portMappings": [
{
"containerPort": 80,
"hostPort": 80
}
],
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "awslogs-wordpress",
"awslogs-region": "us-west-2",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "awslogs-example"
}
},
"memory": 500,
"cpu": 10
},
{
"environment": [
{
"name": "MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD",
"value": "password"
}
],
"name": "mysql",
"image": "mysql",
"cpu": 10,
"memory": 500,
"essential": true,
"logConfiguration": {
"logDriver": "awslogs",
"options": {
"awslogs-group": "awslogs-mysql",
"awslogs-region": "us-west-2",
"awslogs-stream-prefix": "awslogs-example"
}
}
}
],
"family": "awslogs-example"
}In the Amazon ECS console, the log configuration for the wordpress container is specified as shown in the image below.
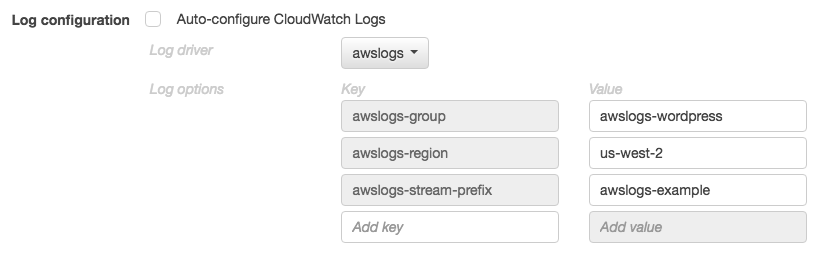
After you have registered a task definition with the awslogs log driver in a container definition log configuration, you can run a task or create a service with that task definition to start sending logs to CloudWatch Logs. For more information, see Run a standalone task and Creating an Amazon ECS service.
Viewing awslogs container logs in CloudWatch Logs
For tasks using the EC2 launch type, after your container instance role has the proper permissions to send logs to CloudWatch Logs, your container agents are updated to at least version 1.9.0, and you have configured and started a task with containers that use the awslogs log driver, your configured containers should be sending their log data to CloudWatch Logs. You can view and search these logs in the console.
To view your CloudWatch Logs data for a container from the Amazon ECS console
- Open the Amazon ECS console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/ecs/.
- On the Clusters page, select the cluster that contains the task to view.
- On the Cluster: cluster_name page, choose Tasks and select the task to view.
- On the Task: task_id page, expand the container view by choosing the arrow to the left of the container name.
- In the Log Configuration section, choose View logs in CloudWatch, which opens the associated log stream in the CloudWatch console.
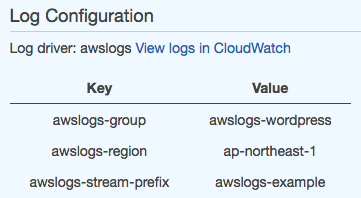
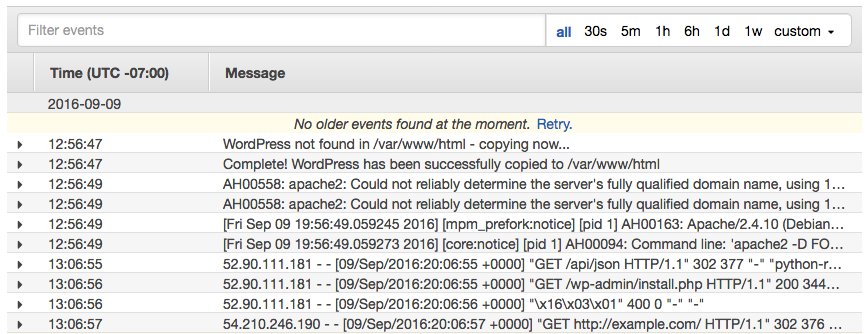
To view your CloudWatch Logs data in the CloudWatch console
- Open the CloudWatch console at https://console.aws.amazon.com/cloudwatch/.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Logs.
- Select a log group to view. You should see the log groups that you created in Creating a log group.

- Choose a log stream to view.
'AWS > ECS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [AWS ECS] How to Create a Security Group? (0) | 2022.03.23 |
|---|---|
| [AWS ECS] How to create a Key Pair in ECS? (0) | 2022.03.23 |
| [AWS ECS] How to Create an IAM user (0) | 2022.03.23 |
| [AWS ECS] Create AWS IAM (0) | 2022.03.22 |
| [AWS ECS] Amazon ECS Basics (0) | 2022.03.22 |