A tree is actually a type of graph, but not all graphs are trees. Simply put, a tree is a connected graph without cycles.
A graph is simply a collection of nodes with edges between (some of) them.
- Graphs can be either directed (like the following graph) or undirected. While directed edges are like a one way street, undirected edges are like a two way street
- The graph might consist of multiple isolated subgraphs. If there is a path between every pair of vertices, it is called a "connected graph."
- The graph can also have cycles (or not). An "acyclic graph" is one without cycles.
In terms of programming, there are two common ways to represent a graph.
Adjacency List
This is the most common way to represent a graph. Every vertex (or node) stores a list of adjacent vertices. In an unlimited graph, an edge like (a, b) would be stored twice: once in a's adjacent vertices and once in b's adjacent vertices.
A simple class definition for a graph node could look essentially the same as a tree node.
public class Graph {
public Node[] nodes;
}
class Node {
public String name;
public Node[] children;
}The Graph class is used because, unlike in a tree, you can't necessarily reach all the nodes from a single node.
You don't necessarily need any additional classes to represent a graph. An array (or a hash table) of lists (arrays, array lists, linked lists, etc) can store the adjacency list. The graph above could be represented as:
0: 1
1: 2
2: 0, 3
3: 2
4: 6
5: 4
6: 5
This is a bit more compact, but it isn't quite as clean. We tend to use node classes unless there's compelling reason not to.
Adjacency Matrices
An adjacency matrix is an NxN boolean matrix (where N is the number of nodes), where a true value at matrix[ i ][ j ] indicates an edge from node i to node j. (You can also use an integer matrix with 0s and 1s.)
In an undirected graph, an adjacency matrix will be symmetric. IN a directed graph, it will not (necessarily) be.
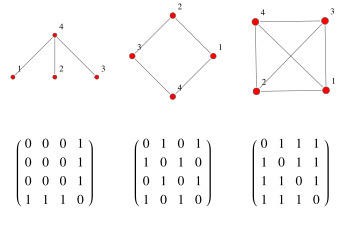
The same graph algorithm that are used on adjacency lists (breadth-first search, etc.) can be performed with adjacency matrices, but they may be somewhat less efficient. In the adjacency list representation, you can easily iterate through the neighbors of a node. In the adjacency matrix representation, you will need to iterate through all the nodes to identify a node's neighbors.
'Algorithms and Data Structures > Data Structures' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Object-Oriented Design (0) | 2022.06.24 |
|---|---|
| [Data Structures] Graph Search (DFS and BFS) (0) | 2022.05.29 |
| [Data Structures] Tries (Prefix Trees) (0) | 2022.05.27 |
| [Data Structures] Binary Heaps (Min-Heaps and Max-Heaps) (0) | 2022.05.26 |
| [Data Structures] Binary Tree Traversals with Implementations (0) | 2022.05.25 |